Your donation will support the student journalists of Fossil Ridge High School. Your contribution will allow us to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs.
MUN simulates Yugoslav Crisis, 1995
March 2, 2019
Model United Nations at Fossil has a major component of media made up of the TV program and Etched in Stone.
On Saturday March 2, Fossil Ridge High School is hosting their annual Model United Nations conference. The scenario is based on past events, but does not reflect the true actions of the countries involved. Students are acting as delegates from the nations involved in the crisis with 106 delegates from schools across Colorado. The following article does not reflect actual events and is only a simulation.
The background of the Yugoslav Crisis, 1914-1994
In 1914, at the start of World War I, The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was formed. Under the dictatorship of the Ustaše, a fascist Croatian party, Serbians, Croatians, and Slovenes lived under the rule of the Yugoslavian president. Then, in 1941, he was killed. The new president excluded fascists from all positions of power, creating tension. Upset with the exclusion of fascism, Nazi Germany and their Italian allies invaded Yugoslavia and returned power to Ustaše in most provinces. They immediately begin the massacre of ethnic Serbs.
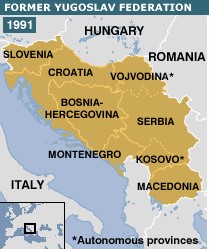
The former Yugoslav Federation of 1991.
After Germany’s loss in World War II, Ustaše lost their backing from the Nazi party. Shortly after, the Yugoslavia monarchy was replaced with a Federal Republic and Josip Broz Tito was appointed president for life. With a Croatian father and a Serbian mother, Tito appealed to both sides of the conflict. President Tito ruled over all of Yugoslavia, a country composed of the following regions: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, and Macedonia.
1980 marked the end of Tito’s leadership. His successor, being a weak leader, left the true power in the hands of the individual regions. The economy had just crashed as a result of the end of the Cold War, leading to ethnonationalism, a common sensation after any economic crisis. The people were putting their faith in the government and unknowingly creating a perfect storm.
In 1987, Kosovo, a province of Serbia, was in the thick of an ethnic conflict. Kosovar Serbs claimed Kosovar Albanians were taking their jobs and, still suffering from the effects of the economic crash, felt threatened and were looking for a scapegoat. As a result, they massacred the Albanians. Miloševič, the head of the Yugoslavian government, was sent in to decrease tension. An ethnic Serb himself, Miloševič’s presence only elevated conflict. Come 1989, Miloševič, now president of Serbia, replaced the presidents of Kosovo and Vojvodina, autonomous provinces within Serbia, as well as Montenegro, with his allies. A peaceful hunger strike of Albanian miners turned deadly, leading to Albanian whispers of hopes of independence.

The Ustaše flag of the 1940’s. This flag was emulated by Tudman in 1990.
In nearby Croatia, Franjo Tudman was selected in the 1990 election. A big nationalist, Tudman rejected communist ideals. He switched the Croatian flag to look similar to the Ustaše flag, upsetting ethnic Serbs living in Croatia. Though currently protected by the rules of the Yugoslavian government, the ethnic Serbs were aware of the impending secession of Croatia from Yugoslavia. In an attempt to prevent this, as it would have left the Serbs at the mercy of the Croatians who had a history of hate against them, the Serbs blockaded major roads in what came to be known as the Log Revolution. Because of their similar interests, the Yugoslav National Army (JNA) supported the ethnic Serbs. The Serbian revolutionaries renamed themselves the “Republic of Serbian Krajina.”
As the structure of Yugoslavia began to waver and many of the republics that were once a part of it recognized this, talk of independence from the larger republic became more commonplace. At the end of 1990, Slovenia became the first republic to hold a referendum on independence, which passed with almost 95% support. Yugoslavia declared a state of emergency, as they feared further declarations of independence—and with good reason. In May 1991, Croatia followed in declaring independence. The two republics fought Yugoslav soldiers for several months before signing a peace treaty that delayed their moving towards independence.
Meanwhile, throughout 1990 and 1991, the Republic of Serbian Krajina continued to fight for and increase their property throughout Croatia, even in non-Serbian-majority towns. The JNA allowed the Serbs to continue pushing through the republic, despite the fact that they were technically only in Croatia on a “peacekeeping” mission. Further adding to Yugoslavia’s downward spiral, Macedonia, in September 1991, also declared independence.
Miloševič rejected a peace deal that would have assuaged these conflicts because it would have broken up the rest of Yugoslavia, and the United Nations intervened in 1992, stilling the fighting between the Croats and Serbs.
However, Yugoslavia was by no means free of ethnic tension. Bosnia and Herzegovina were in a unique position, as the republic contained large populations of Catholic Croats, Orthodox Christian Serbs, and Muslim Bosniaks. The Bosnian Serbs declared themselves the Republika Srpska and pushed for Bosnia to remain in Yugoslavia, while the Bosniaks held their own independence referendum in 1992. This passed.

The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia flag.
In April of 1992, the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia released their communist ideals and became the Republic of Yugoslavia. However, they maintained their claims on their former republics. Simultaneously, the Republika Srpska began attacking Bosniak Muslims in and around the Bosnian capital, Sarajevo. To add a third level to the conflict, the Croats in Bosnia declared themselves the Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia and began trying to unify with Croatia.
In 1993, the UN placed several cities in Bosnia under their protection for the sake of their citizens. A proposed peace plan would have divided Bosnia into ethnic provinces, but the Republika Srpska refused to accept a course of action that would have lost them any of their land gains. Yugoslavia backed the Republika Srpska’s decision.
That was when the Republika Srpska began targeting civilians outside of Sarajevo, drawing the attention in early 1994 of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. NATO demanded that Srpska remove their weapons from outside the city, which drew the attention of Russia, as they believed NATO was overstepping their role in global politics. Russia promised Radovan Karadžić, president of Srpska, that Russia would help them if NATO moved to remove their weapons from the hills, and Ratko Mladić, a commander in their army, attacked a UN safe area. The UN thus approved an airstrike against Srpska, and resultantly, Mladić took UN hostages.

The studio functions with the help of the behind the scenes members of the crew.
The Media: The behind the scenes heroes
The Fossil media program has a long-standing tradition of enhancing the experience of the MUN conference. With hourly broadcasts and field crew interviews with delegates, the TV program stays busy.
Katherine Johnson, Co-Producer for the event, ensures the media aspect runs smoothly. Additionally, she oversees communication with the MUN delegates. “A big challenge is communication with such a large crew… We’re spread out throughout the entire school. There’s also a lot of factors that could go wrong,” she commented.
However, looking forward, Johnson is optimistic. “We have a good crew with some underclassmen in leadership positions being taught by upperclassmen who have been in this role for a long time,” she said. “People like to branch out from their usual roles so it’s really cool. MUN is a fun time and we’ve worked really hard and it’ll be a cool time.”
MUN is full of twist and turns, complicating the roles of the media. Isabella Mahal and Liam H. Flake work on the teleprompter, constantly adapting to the incoming information from delegates and press releases. Main anchors include Olivia Doro, Sebastian Mahal, and Blake Tracer. With the Russian bias, Paisley Perlic and Alex Vantellingen will be on screen.
Behind the scenes, a 70 person crew works tirelessly to enhance the experience of the MUN delegates. Everyone from personal assistants to media leads plays a crucial role in the accuracy and authenticity of broadcasts and news releases.

Radovan Karadžič states her argument for a strong central government.
Pan Yugoslav Council, 10:27 a.m.
The smallest council, the Pan Yugoslav is working to combat division of the Yugoslav country’s regions. Each region came with strong ideals and is reluctant to surrender. It consists of five delegates from various regions in Yugoslavia.
Dominating the room is Milan Martić, a Croatian Serb. She is adamant that Yugoslavia belongs to the Serbs. Martić feels it would be ideal to send other minorities to Serbia. “We must remain strong and we must remain united,” she said.
Radovan Karadžič of Bosnia believes the media is propaganda. She works to avenge the genocide of all minorities and feels strongly about a federalist Yugoslav government. Ibrahim Rugova of Kosovo, on the other hand, considers autonomy and the equality of Kosovo to Serbia the only solution. He feels NATO would overstep and therefore is against their intervention.
With educated and passionate delegates, the small council has engaged in several unmoderated caucuses and become heated in a stalemate with little progress.
Word has been delivered that the United States is supplying arms to various countries. Stay tuned for updates.
BREAKING: Hostage taken and USA Deploys 5,000 troops, 10:38
In an attempt to free Riley Lee, the hostage taken by a mysterious hooded figure, the United States has mobilized 5,000 troops. With hopes of stabilizing the region, the delegate stated, “Military force is the only way.”
BREAKING: Hostage allegedly killed, Britain blames Serbia, 11:13
After NATO was accused of killing the hostage, Britain quickly turned fingers to Serbia. Claiming they deployed troops only as a peace keeping tactic, Britain asserted the Serbs acted independently from the wishes of Britain.

Serbia denies accusation of killing of the hostage, 11:38
As Serbia is not in attendance, representative Milan Martić spoke on their behalf. “We deny this accusation outright,” she said. Britain asserted the Serbs were responsible for the death of hostage Riley Lee. Serbia rejected the assertion, saying “We had no direct involvement with the kidnapping or killing and hadn’t heard anything about it.” Martić is a strong advocate for the Serbs, a Croatian Serb herself. With a history of defending Yugoslavia as “the rightful land of the Serbs,” Martić was expected to deny Britain’s accusation.
Live-stream link
The media has been broadcasting newscasters and press releases throughout the conference. Find the live link here.

The conference has been cut short in the midst of debate regarding WWIII.
World War III, the eradication of Serbia, and inclement weather: Conference cut short
Following the eradication of Serbia and right as World War III was called, the conference has been cut short. Delegates needing to travel to Denver and cities in the mountains were required to leave early as the weather in Fort Collins worsens. The awards ceremony is being held in the Performing Arts Center and the results are as follows are as follows:
Beginner Council:
Best Delegation: France
Outstanding Delegation: Kosovo
Best Position Paper: Oman
Intermediate Council:
Best Delegation: Russia
Outstanding Delegations: Pakistan and Canada
Honorable Mention: Tunisia, Spain, United States
Best Diplomatic: Pakistan
NATO:
Best Position Paper: Norway
Honorable Mention: Norway
Outstanding Delegation: Bosnia
Best Delegate: United States
Pan Yugoslav Council:
Best Position Paper: Milan Martić
Third Place Honorable Delegate: Milan Martić
Outstanding Delegate: Petro Povich
Best Delegate: Korasic
Media Best Delegate:
Beginner Security Council: Russia
Intermediate Security Council: India
Pan Yugoslav Council: Srpska
NATO: France



Liz Taylor • Mar 18, 2019 at 9:50 pm
Yes, the MUN kids worked insanely hard on this production and possibly I have commented on this topic too late but, for years as a student within the media crew and I have found myself feeling completely and totally invisible. Guess what, that’s our role – to be lost within the blur of a production. Let yourself keep this in mind, we don’t do it for attention and nor do they but for the first time in quite a long time we were seen as something a bit more relevant than just a camera and a few odd kids running around like chickens without heads. This is brilliantly written and I do stand by the fact that nothing needs to be changed.
Mackenna Riek • Mar 4, 2019 at 2:47 pm
This article displays false and quite frankly narcissistic information. There was so much work done by others that you COMPLETELY ignored. There should not be as much credit to Media as there is. Model UN isn’t mentioned but they HOSTED it. I’m not affiliated with model UN at all, but I know they put hard work into this and all you can credit them for is a caption of a picture that they aren’t even in. Being such a well known platform, at least try to put the truth out.
(P.S. It was created in 1918. And maybe fix that flag.) 🙂
Joshua Mayer • Mar 4, 2019 at 12:54 pm
Firstly, the background guide here is wrong, if you’d like a link to a background guide with hours of research and writing involved please read the background guide section of the paper in the following link. (Provided by FRHS MUN) https://docs.google.com/document/d/16gRklNMSdRa8Dm6Wwr3uDQvQEDSzYe3gIRSIZCRGKFk/edit?usp=sharing
The Model United Nations club did the brunt of the work for this club with hours upon hours of preparation, research, and physical set up being pressed into the event. Media did do work, and they were integral to the experience, but ignoring the hours of work of the MUN club is a mistake. Rather than recognizing the effort of just one group involved, all of the efforts of all of the groups involved ought to be mentioned, and this article fails to do so. While the article goes out of its way to mention as many of the media members as possible (and those mentioned did do fantastic work) not a single member of the MUN club was mentioned. This should be corrected.
Ryan Green • Mar 4, 2019 at 12:53 pm
I don’t feel like this article accurately addresses how this conference was ran. Media was a massive help towards enhancing, and creating the atmosphere for the event, but without a doubt it was the FRHS MUN Club that ran the event, not the Media. This article doesn’t give nearly enough mention to the hard working, committed Model United Nations club in this school.
I want to make clear that I love the work the media did for our event, but I feel like it’s wrong to label the media the “Behind the scenes heroes” and to call Katherine Johnson “Co-Producer for the event.” Josh Mayer came up with this scenario, and slaved over the background guide for hours on end. Matt Mayer, Sawyer Shireman, and Abigail Riley were the secretary generals, and the backbone of the conference. Mr. Huckaby put up with all of us for months on end, and masterfully steered us out of debt. Dozens of our aides, crisis staff, presiding officers, and more were essential to this event. None of these fantastic individuals, or our club as a whole are mentioned here. I feel like the main people who ran this event were entirely ignored.
I would like to see this article revised to accurately capture the organization of this event. Once again, Media were an excellent addition to this club, and we appreciate their tireless work to truly set us apart from the competition. However, the FRHS MUN Club ran this event. You’re more than welcome to reach out to us if you would more information about the event. We host meetings every Thursday at Lunch, room W106.